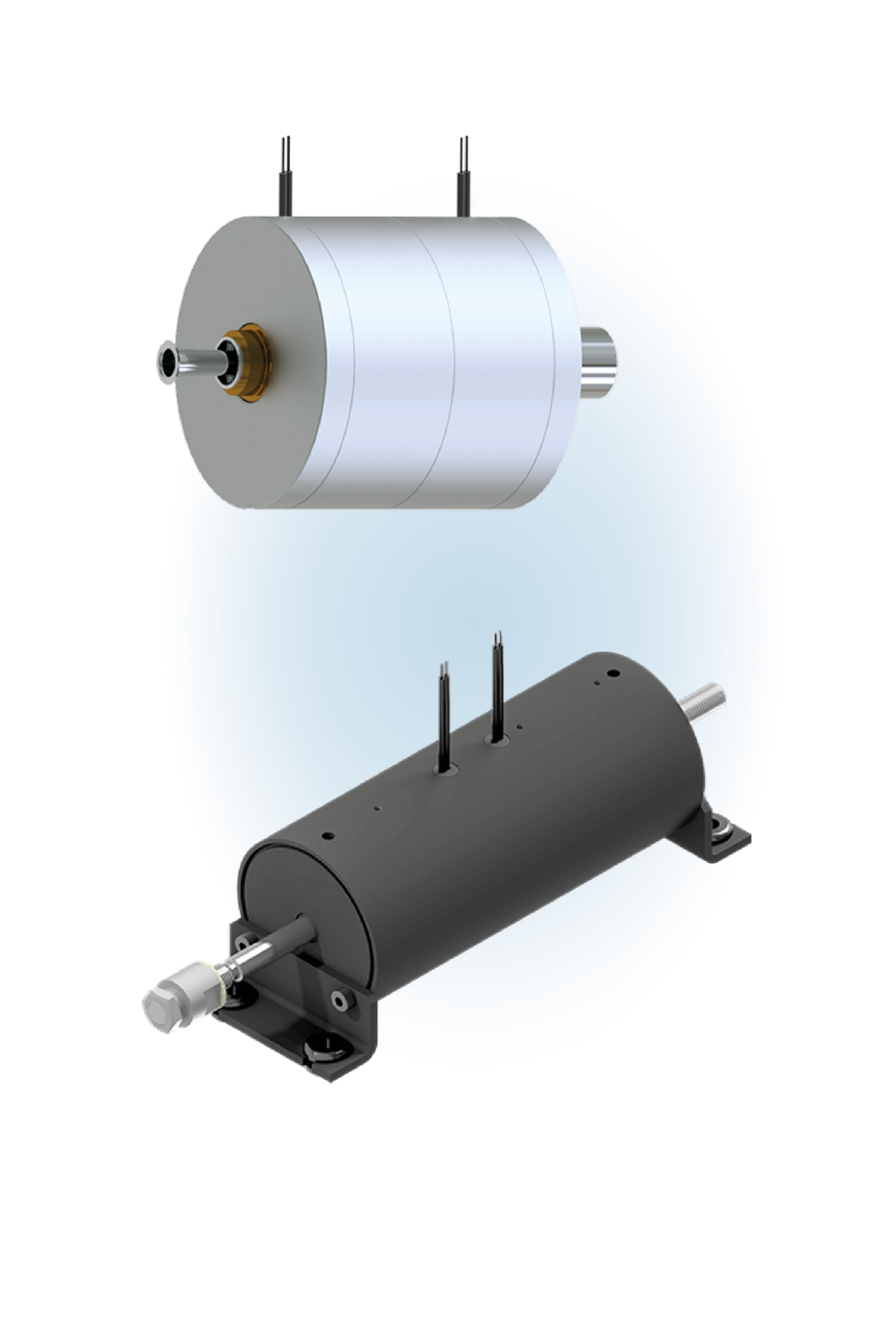
Rapid development, validation & industrialisation.
Double-stroke solenoids
Are you looking for a reliable partner for high-quality double-stroke (double acting) solenoids? You are in good hands with Magnetbau Schramme! As a specialist in the development and production of customised double-stroke solenoids, we offer innovative and precise solutions that are precisely tailored to your specific requirements.
You can rely on our many years of experience and expertise to make your project a success.

Development and production of double solenoids
Our performance and expertise. Your success.
Magnetbau Schramme is your experienced partner for the development and series production of double-stroke solenoids. With our comprehensive technical know-how and many years of expertise, we realise customised solutions that are precisely tailored to your individual requirements. From the initial idea to series production, we accompany you through the entire development process and ensure smooth implementation in all phases.
Contact us today and let our experts advise you individually.
Please note!
Please note that we do not have any standard products. The following double-stroke solenoids are merely examples of customer projects realised in series production.
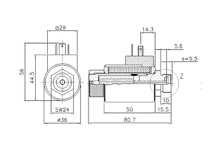
Technical data - Double-stroke solenoids
Experience the plenty of customised options.
A double-stroke solenoid is an electromagnetic actuator in which the armature can move to two positions. The armature can achieve two different stroke lengths, i.e. it can either stop in a middle position or in a further end position, depending on the control system. It can have two or more coils that allow the armature to be pulled to two different distances. The backward movement of the armature is ensured either by external mechanical restoring forces or by integrated elements such as springs. These solenoids enable precise and repeatable movements and are used in systems that require precise control of mechanical processes, for example in automation technology or for valve controls.
Do you have any questions about our technical data or other details you would like to discuss? Please feel free to contact with us.
| Construction size | No limitation, up to a max. construction weight of 15kg. |
| Nominal voltage range | 6V, 12V, 24V, 36V and others |
| Magnetic stroke | up to 40mm |
| Lifting force | up to 1000N |
| Protection class / protection type | up to IP6K9K |
| Electrical connection | Free stranded wires, surface-mounted connectors, integrated (moulded) connectors, etc. |
Development & series production
Magnetbau Schramme is your specialist in the development and production of customised switching and control solenoids.


Alexander Grischin
Sales Manager
- Requirements analysis
- Feasibility assessment
- Product concept
- Calculation, simulation
- Individual parts, assemblies
- Final assembly
- Functional test
- Proof of technical suitability
- Tools, equipment
- Quality, logistics
- Procurement, production
- Assembly, EOL testing
More information about double-stroke solenoids
How a double-stroke solenoid works
- The way a double-stroke solenoid works is based on the principles of electromagnetism. As soon as current flows through a coil of the solenoid, a magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field exerts a force on the armature, which is located inside the solenoid. The strength of this force depends on the current supply. The movement of the armature can be reversed by two mechanisms. An integrated or external restoring force, usually by a spring, returns the armature to its initial position as soon as the current is switched off.
Designs and types of double solenoid
- Square double-stroke solenoids: These solenoids have a rectangular cross-section. Thanks to their compact design, they are ideal for applications where space is limited. They can be easily integrated into various customer applications and offer reliable switching movements.
- Round double-stroke solenoids: These solenoids have a cylindrical cross-section and are usually more cost-efficient, as they can be manufactured with moulded housing components. The round design ensures a uniform distribution of the magnetic field, which can have a positive effect on the function of the double-stroke solenoid.
Double-stroke solenoid performance parameters
- Magnetic force: The magnetic force is the force that the double-stroke solenoid can exert on the armature. This force depends on many parameters, including the electrical power and the design of the coil.
- Stroke: The stroke describes the total distance travelled by the moving armature.
- Duty cycle: The duty cycle (ED) describes the period of time during which the double-stroke solenoid is energised without overheating. It is given as a percentage and defines the ratio of operating time to idle time. A duty cycle of 100 % means continuous operation, while a lower duty cycle indicates temporary pauses to prevent overheating.
- Response time: The response time is the time it takes for the solenoid to change from the starting position to the maximum stroke position. A short response time is important for applications that require a fast response and high switching frequency, e.g. in automation or sorting processes.
- Current consumption: This parameter specifies the current consumption of the double-stroke solenoid. It influences the size of the current source and the efficiency of the system. A low current consumption is particularly advantageous for energy-efficient applications, while a higher current consumption is often associated with a stronger magnetic force.
- Service life: The service life describes the number of cycles that the double solenoid can reliably perform. It is an indicator of the longevity and reliability of the solenoid in continuous applications and depends, among other things, on the materials used, the quality of the bearings and the mechanical load.
Structure of the double-stroke solenoid
- Housing: The housing encloses the entire assembly and protects the components from external influences such as dust, moisture or mechanical loads. The housing also ensures mechanical stability.
- Coil: The coil usually consists of a wire winding with a magnetisable core in the centre. The wire used for the coil is usually made of a highly conductive material such as copper. The number of turns in the coil, the current strength and the shape of the coil influence the properties of the magnetic field generated
- Armature: The armature is the movable element in the solenoid that moves linearly under the influence of the generated magnetic field. It consists of a ferromagnetic material that reacts to the magnetic field of the coil. The armature is set in motion by the magnetic field of the coil, which generates the stroke.
- Iron core: The magnetic core is the stationary, ferromagnetic material inside the coil that amplifies the magnetic field and concentrates the magnetic force on the armature. It ensures that the magnetic field is effectively transferred to the armature, enabling the stroke movement.
- Return mechanism: A mechanical spring is often integrated, which pushes the armature back into its initial position after the magnetic field is switched off. This spring resets the armature when the current is switched off. In some designs there is no spring. Instead, the reset is ensured by external forces.
- Electrical connection: These components are used for the electrical connection of the reversing solenoid to the power supply. They can be either simple terminals or standardised plug connections.
Double-stroke solenoid applications
- Automation technology: Double-stroke solenoids are used in automatic doors, sliding gates or flaps of machines and systems to open and close them precisely. Double-stroke solenoids are also frequently used in machines and production lines to move components or workpieces to several predefined positions. For example, in punching or cutting machines where tools have to be moved to different positions.
- Paper processing: In the printing industry, double-stroke solenoids can be used to move rollers or paper guides between different stroke lengths, depending on the requirements of the printing process. They help to precisely control the paper transport or to move print heads to different positions.
- Medical technology: Double-stroke solenoids can be used in laboratory and analytical equipment to precisely dispense or move samples or liquids, and in medical devices to control safety mechanisms or activate locking devices.
- Safety technology: In access control systems or electronic locking systems, double-stroke solenoids can be used to lock or unlock doors or mechanisms between several positions. Here, the solenoid is used to move locking bolts into different positions.
- Vehicle technology: Double-stroke solenoids can be used in mechanical clutches where different clutch stages or shift positions need to be activated. They are also used in electronic gear levers that require precise gear changes.
- Textile machinery: In textile processing, double-stroke solenoids can be used in machines that control or lift fabric webs by allowing movement between different positions to correctly position the fabric.
Double solenoid control and regulation
- Electronic control: The electronic control of a double-stroke solenoid regulates the power supply to the solenoid coils to control the movement of the armature. Simple systems use switches, relays or transistors for current control and pole reversal. More complex control systems integrate microcontrollers or PLCs that enable programmable sequences and tune the solenoid to external signals in real time. They can precisely manage operating modes such as forward/reverse motion and timing.
- Pulse width modulation (PWM): PWM control regulates the power of the double-stroke solenoid by rapidly switching the current on and off with a variable pulse length. This controls the average voltage, enabling precise control of stroke and force.
- Sensor integration: Sensors are integrated into assemblies to monitor the position of the armature or the applied force. Position sensors such as Hall sensors or potentiometers provide feedback for precise control of armature position, while force sensors measure the applied force. PID controllers use the feedback to dynamically adjust the power supply and ensure smooth, precise movement, e.g. in robotics or safety mechanisms.
Environmental requirements Double-stroke solenoid
- Temperature range: Double-stroke solenoids must work reliably in a wide temperature range from -40 °C to +150 °C without impairing their performance. High operating temperatures can lead to overheating and loss of magnetic properties, while very low temperatures can make the material structure brittle. It is therefore important that the materials and design of the double-stroke solenoid are suitable for the specified temperature range.
- Types of protection: Depending on the application environment, double-stroke solenoids are equipped with different types of protection (e.g. IP protection classes) to protect them from dust, moisture and other environmental influences. These protective measures are crucial to ensure the long-term functionality and reliability of the solenoid in demanding operating conditions.
Double-stroke solenoids - Questions & Answers
What is the difference between a reversing solenoid and a double-stroke solenoid?
A reversing solenoid moves the armature in two opposite directions (forwards and backwards) between two fixed end positions, controlled by two separate coils. A double-stroke solenoid, on the other hand, moves the armature between two different stroke lengths (shorter and longer stroke), whereby it can move to several positions (usually three: starting, intermediate and end position). The reverse stroke solenoid works bidirectionally, while the double-stroke solenoid is used for different stroke distances within the same direction of movement.
In which areas is the double-stroek solenoid most frequently used?
Double-stroke solenoids are mainly used in automation technology, where they are used for precise motion control in machines and robots. They are also frequently used in mechanical and plant engineering and other mechanical components. Other areas of application include the manufacturing and packaging industries, where they are used for positioning and lifting applications.
Can double-stroke solenoids be used in harsh environments?
Yes, double-stroke solenoids can be used in harsh environments as long as they are equipped with appropriate protection classes, such as IP protection classes that protect against dust and moisture. They should also use materials that are corrosion-resistant and can withstand temperature and pressure fluctuations. In applications such as automation technology or the manufacturing industry, double stroke solenoids are often designed for use in demanding environments.
How can I ensure that the double-stroke solenoid does not overheat?
To ensure that the double-stroke solenoid does not overheat, do not exceed the maximum duty cycle (ED) and do not operate the solenoid beyond its specified operating time. Suitable cooling, either through natural ventilation or active cooling measures, can also help to regulate the operating temperature. In addition, the use of temperature sensors to monitor the temperature in real time can be useful to detect overheating at an early stage and take appropriate action.
How does the connection of the double-stroke solenoid to the customer interface work?
The double-stroke solenoid is connected via a technical interface to control units, such as microcontrollers or PLCs, which control the required current direction and pulse width modulation. In addition, mechanical brackets and sensors for position monitoring should be integrated to ensure precise and efficient operation in the customer's overall system.