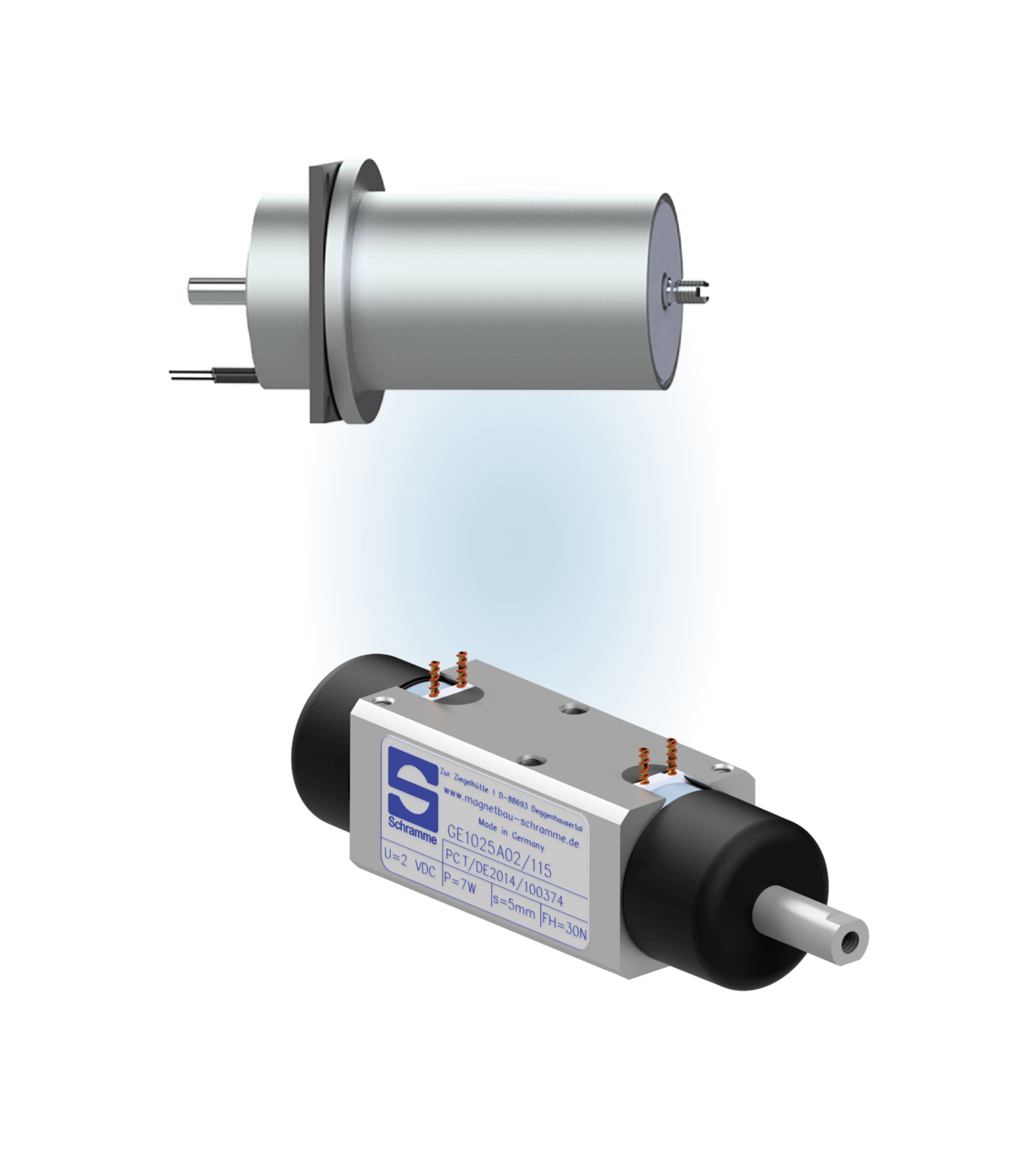
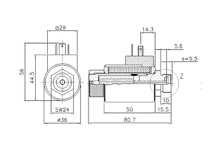
Rapid development, validation & industrialisation.
Reversible solenoids
Are you looking for a reliable partner for high-quality reversible solenoids? Magnetbau Schramme is the right place for you! As a specialist in the development and production of customised reversible linear solenoids, we offer you innovative and precise solutions that are perfectly tailored to your individual requirements.
Rely on our many years of experience and expertise to make your project a success.
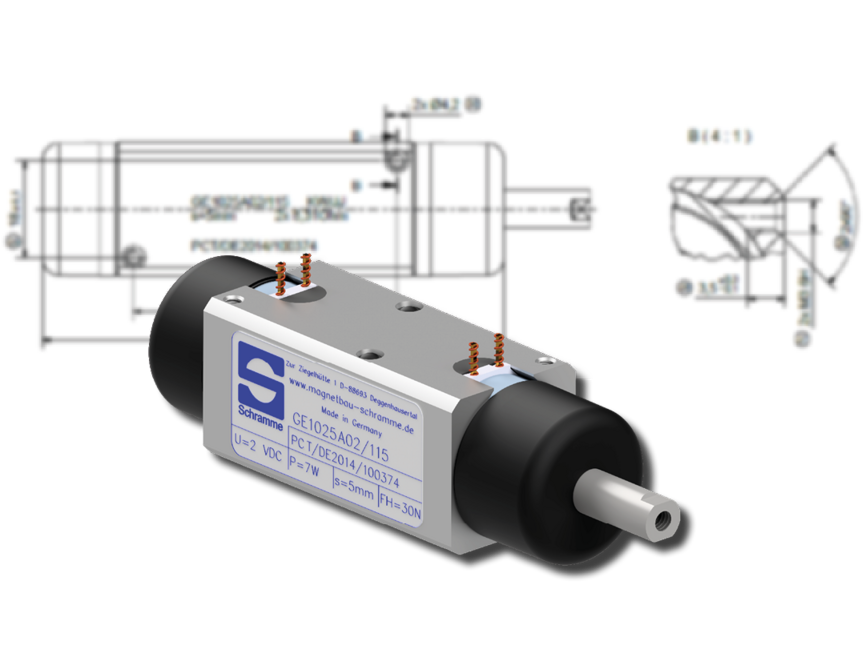
Development and production of reversing solenoids
Our performance and expertise. Your success.
Magnetbau Schramme is your competent partner for the development and series production of reversible solenoids. With our extensive technical expertise and many years of experience, we implement customised solutions that are precisely tailored to your specific requirements. We support you from the initial concept phase through to series production and ensure smooth implementation at every stage of the development process.
Contact us today and get personalised advice from our experts.
Please note!
Please note that we do not have any standard products. The following reversible solenoids are merely examples of customer projects realised in series production.
Technical data - Reversible solenoids
Experience the wealth of different possibilities.
Reversing solenoids are electromagnetic actuators that can switch to two stable end positions, making them ideal for applications where alternating movement between two defined positions is required. They have two coils that move the armature assembly to one position or the other depending on the control. Reversing solenoids from Magnetbau Schramme are characterised by their high switching speed, precise repeat accuracy and robust design, making them reliable in demanding industrial environments.
Do you have any questions about our technical data or other details that you would like to discuss? Please do not hesitate to contact us.
| Construction size | No limitation, up to a max. construction weight of 15kg. |
| Nominal voltage range | 6V, 12V, 24V, 36V and others |
| Magnetic stroke | up to 40mm |
| Lifting force | up to 1000N |
| Protection class / protection type | up to IP6K9K |
| Electrical connection | Free stranded wires, assembled connectors, integrated (moulded) connectors, etc. |
| Special features | Bistable and bidirectional available, highest power density, patented technology |
Development & series production
Magnetbau Schramme is your specialist in the development and production of customised switching and control solenoids.


Alexander Grischin
Sales Manager
- Requirements analysis
- Feasibility assessment
- Product concept
- Calculation, simulation
- Individual parts, assemblies
- Final assembly
- Functional test
- Proof of technical suitability
- Tools, equipment
- Quality, logistics
- Procurement, production
- Assembly, EOL testing
More information about reversible solenoids
How a reversing solenoid works
The functionality of reversing solenoids is based on the principle of electromagnetic attraction, whereby the solenoid alternates between two defined end positions. The solenoid consists of a movable armature and two coils.
- Control of the coils: When current is passed through one of the coils, it generates a magnetic field that pulls the armature in one direction and holds it there. This end position remains stable as long as the coil is energised.
- Changing position: To move the armature to the opposite end position, the current supply to the first coil is interrupted or reduced and the second coil is activated. This creates a magnetic field that pulls the armature into the other position.
- Resetting without a spring: Unlike conventional solenoids, which often require a spring for resetting, the reversing solenoid switches autonomously between the end positions through the targeted use of both coils, without the need for a mechanical reset.
- Advantages of the design: This design enables fast and precise switching, high repeat accuracy and the ability to remain permanently stable in both end positions. If permanent magnets are integrated, the end positions can even be kept de-energised.
Designs and types Reversing solenoid
- Square reversing solenoids: These solenoids have a rectangular cross-section. Thanks to their compact design, they are ideal for applications where space is limited. They can be easily integrated into various customer applications and offer reliable switching movements.
- Round reversing solenoids: These solenoids have a cylindrical cross-section and are usually more cost-efficient, as they can be manufactured with moulded housing components. The round design ensures a uniform distribution of the magnetic field, which can have a positive effect on the function of the reversing solenoid.
Reversing solenoid performance parameters
- Magnetic force: The magnetic force is the force that the reversing solenoid can exert on the armature to move it between the two end positions. This force depends on many parameters, including the electrical power and the design of the coil.
- Stroke: The stroke describes the distance travelled by the moving armature between the two end positions.
- Duty cycle: The duty cycle (ED) describes the period of time during which the reversing solenoid is energised without overheating. It is given as a percentage and defines the ratio of operating time to rest time. A duty cycle of 100 % means continuous operation, while a lower duty cycle indicates temporary pauses to prevent overheating.
- Response time: The response time is the time it takes for the solenoid to switch between the two end positions. A short response time is important for applications that require a fast response and high switching frequency, e.g. in automation or sorting processes.
- Current consumption: This parameter specifies the current consumption of the reversing solenoid. It influences the size of the current source and the efficiency of the system. A low current consumption is particularly advantageous for energy-efficient applications, while a higher current consumption is often associated with a stronger magnetic force.
- Service life: The service life describes the number of switching cycles that the reversing solenoid can reliably perform. It is an indicator of the longevity and reliability of the solenoid in continuous applications and depends, among other things, on the materials used, the quality of the bearings and the mechanical load.
Structure of the reversing solenoid
- Housing: The housing encloses the entire mechanism and protects the internal components from external influences such as dirt, dust or moisture. It is often made of metal or plastic and provides the necessary stability.
- Armature: The armature is the movable part of the reversing solenoid, which is moved back and forth between two defined positions. It is usually made of a ferromagnetic material and is pulled into the respective end position by the magnetic field of the coils.
- Coils: The reversing solenoid has two separate coils. When one coil is activated, it generates a magnetic field that pulls the armature into the corresponding end position. By changing the coil current, the armature can be moved back and forth between the two positions.
- Yoke: The yoke consists of a magnetically conductive material and efficiently conducts the magnetic field of the coils to the corresponding areas. It ensures optimum transfer of the magnetic field to the armature.
- End position stops: These components define the two end positions of the armature and ensure that the movement stops precisely. They ensure a clear and defined position for the armature when it is attracted by either the first or the second coil.
- Electrical connection: The electrical connections link the coils to the external control unit or power source. The current is fed into the coils via these contacts, which generates the magnetic field.
Reversible solenoid applications
- Automation technology: Reversing solenoids are often used in automated production lines to control movements, such as the opening and closing of grippers, flaps or other mechanical devices.
- Mechanical engineering: They are used in machines and devices that require precise control of movements, for example in presses, conveyor systems and automatic assembly machines.
- Positioning systems: Reversing solenoids are used to enable precise positioning of components in machine tools and other industrial applications
- Switching systems: They are used in electrical switching systems to control and switch electrical connections, for example in relays or switch boxes.
- Medical technology: In medical technology, reversing solenoids can be used in devices that require precise movements, such as in robots for surgical procedures or in imaging devices.
- Vehicle construction: In vehicles, they are used to control various systems such as door locks and seat adjustments.
- Security systems: Reversible solenoids are also used in security systems to control mechanical locks or trigger alarms.
- Robotics: They are used in robotic systems that have to perform precise and repeatable movements, for example in industrial robots or autonomous vehicles.
Control and regulation Reversible solenoid
- Electronic control: Reversible solenoids are usually activated via electronic controls. These controls can be simple switches or complex microcontrollers that regulate the flow of current to the coils of the solenoid. The control system makes it possible to move the solenoid precisely to the desired end positions.
- Pulse width modulation (PWM): A common method of controlling the force and speed of reversing solenoids is pulse width modulation (PWM). PWM allows the strength of the magnetic field to be adjusted, resulting in precise and repeatable control of movements.
- Sensor integration: Various sensors (e.g. microswitches or position sensors) can be integrated to ensure precise positioning and control. These sensors provide feedback on the current position of the armature and enable closed-loop control, which corrects errors and increases accuracy.
Environmental requirements Reversible solenoid
- Temperature range: Reversing solenoids must be able to operate in a wide temperature range, typically -40°C to +150°C, without compromising their performance. High operating temperatures can lead to overheating and a loss of magnetic properties, while very low temperatures can make the material brittle.
- Protection classes: Depending on the application environment, reversible linear solenoids are equipped with different protection classes (e.g. IP protection classes) to protect them from dust, moisture and other environmental influences and to ensure long-term functionality.
Reversible solenoids - Questions & Answers
What is the difference between a double stroke solenoid and a reversing solenoid?
The main difference between a double stroke solenoid and a reversing solenoid is their mode of operation: Reversing solenoids generate movements between two defined end positions by activating two separate coils. This makes reversing solenoids suitable for applications that require precise and repeatable movements. The double stroke solenoid offers two different stroke lengths and can move the armature between a shorter and a longer stroke position.
What is a bistable reversing solenoid and what characterises it?
A bistable reversing solenoid is an electromagnetic component that can hold two stable end positions without being constantly supplied with energy. After a current pulse, it remains in the position reached until another pulse moves it to the other position. This saves energy as no permanent power supply is required to maintain the state. It is characterised by its ability to reliably switch mechanical movements and to be particularly efficient in applications with infrequent switching operations.
What is the difference between a bistable and a bidirectional reversing solenoid?
A bistable reversing solenoid has two stable end positions, which it retains after a single activation until a new current pulse moves it to the other position, making it energy-efficient. A bidirectional reversing solenoid, on the other hand, can move in both directions, but requires continuous energy for control in order to maintain the desired position. The main difference is therefore that the bistable solenoid holds the position even without a continuous power supply, whereas the bidirectional solenoid requires continuous control for each movement.
In which area are reversible solenoids most frequently used?
Reversing solenoids are most commonly used in automation technology, especially in the manufacturing and assembly industry. They are used to control precise movements, such as the opening and closing of grippers, the positioning of components and the switching of mechanical devices. They are also widely used in applications such as robotics, conveyor systems, machine tools and medical technology, where reliable and repeatable control of movements is required.
What advantages do reversible solenoids offer over other types of solenoids?
By activating a winding, the armature is either pulled in one direction or moved in the other direction. The armature moves actively in both directions without the need for mechanical restoring forces (such as a spring). They offer high precision, reliability and flexibility in controlling movements between two fixed positions, making them ideal for applications with specific requirements.