ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certified as developer & producer of electromagnets.
Hydraulics
Discover how our innovative hydraulic solutions and advanced technologies are redefining the drive systems of tomorrow.

Use of electromagnets
Efficiency and precision: hydraulic systems optimise modern drive technologies
Electromagnetic actuators, such as solenoids and linear solenoids, play a crucial role in industrial and mobile hydraulics. They offer precise control, high reliability and compact designs that are perfectly matched to the requirements of modern hydraulic systems.
Application examples for solenoids in hydraulics:
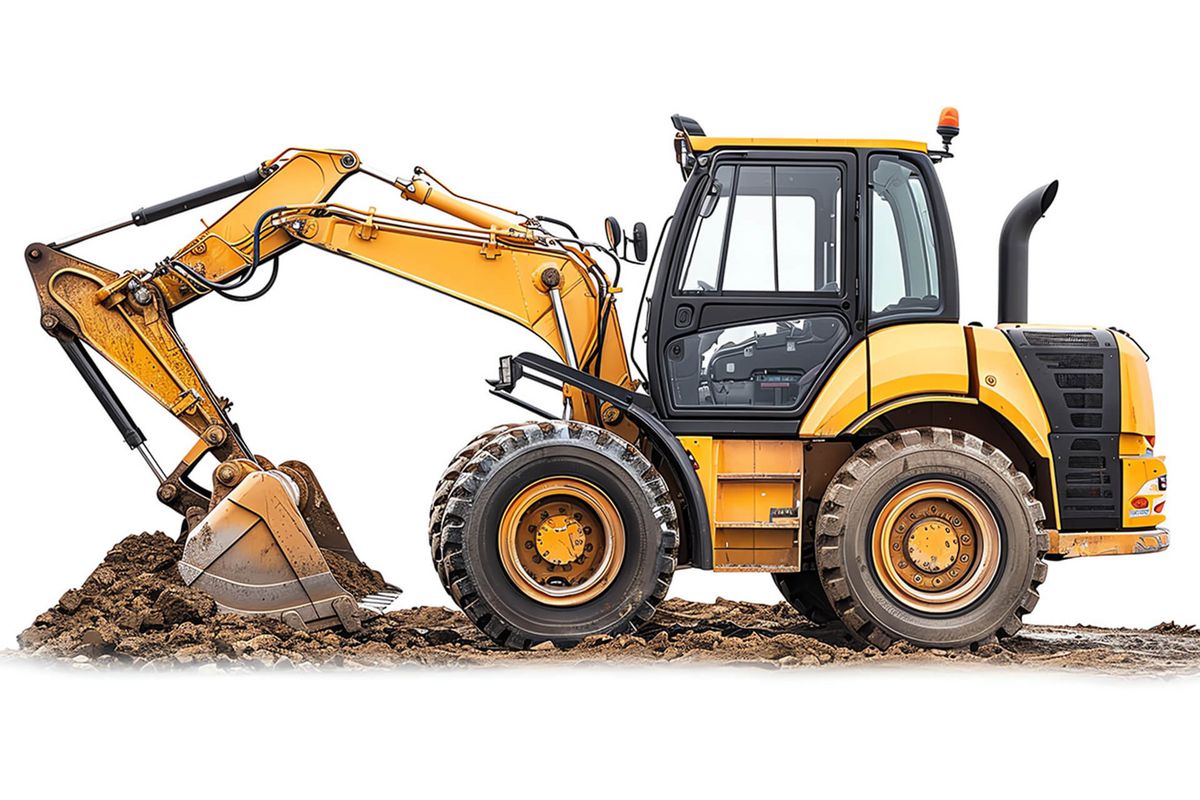
- Switching solenoids for actuating valves in construction and agricultural machinery and similar applications
- Proportional solenoids in mobile hydraulic systems for regulating pressure and flow rate
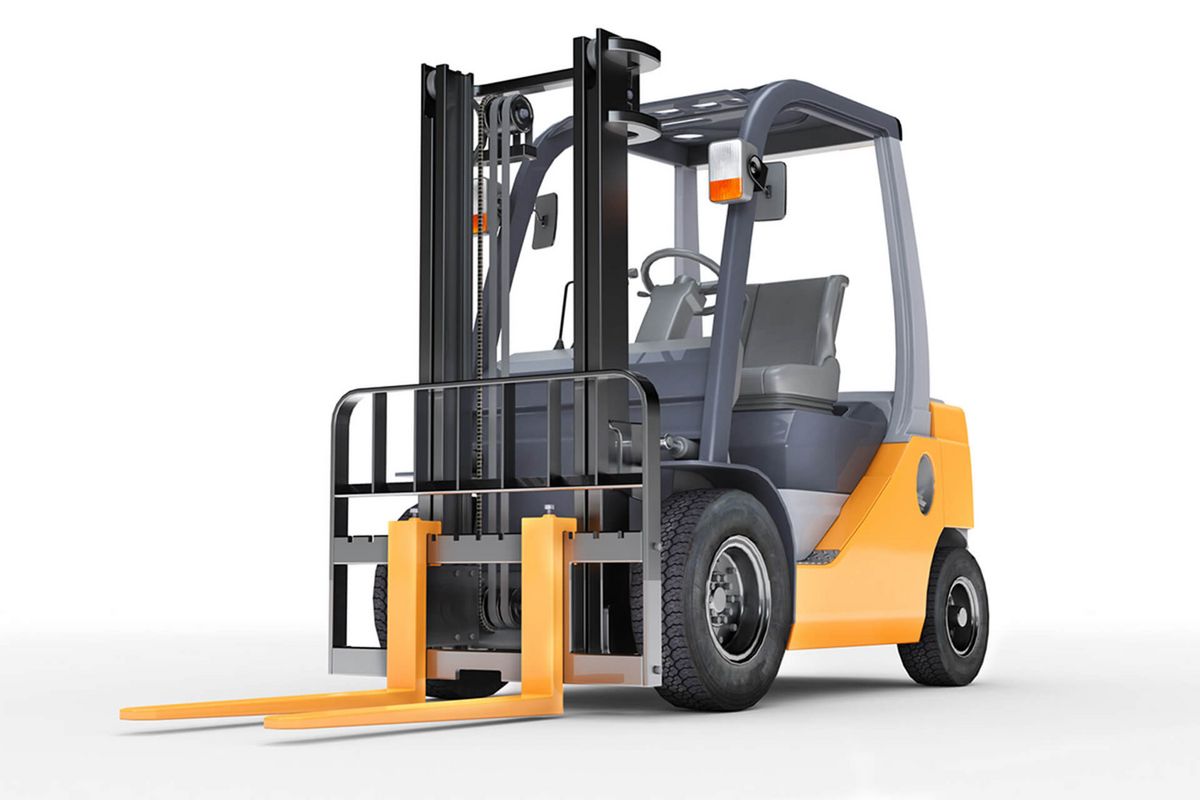
- Linear solenoids in heavy-duty hydraulic systems for lifting and lowering in forklift trucks
- Proportional solenoids in agricultural technology for controlling attachments
- And many more
Precision and reliability in demanding applications
With their ability to actuate valves quickly and precisely, our solenoids increase the efficiency and performance of applications such as construction machinery, agricultural machinery and industrial manufacturing processes. Their robust design ensures reliable operation even under extreme conditions. In addition, they enable innovative solutions to optimise energy consumption and control technologies, making them indispensable components in future-oriented hydraulic systems.
Your advantages with Schramme
Development and production of electromagnets in hydraulics
Magnetbau Schramme is your experienced partner for the development and series production of high-quality electromagnets for hydraulic applications. With decades of expertise, we offer customised solutions that meet the highest standards of precision, efficiency and reliability and can be seamlessly integrated into demanding applications.
From the initial concept phase to series production, we provide you with comprehensive support and efficiently realise individual requirements thanks to flexible manufacturing processes. You can rely on "Made in Germany" quality for innovative solutions in the control and regulation of hydraulic pressures and volume flows.
More than 50 years of experience in the development & series production of electromagnets.
CNC, welding, soldering, injection moulding assembly (ESD / clean room) and much more.


Alexander Grischin
Sales Manager
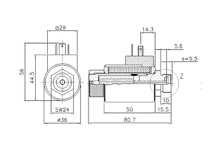
Application example: linear solenoid
Construction and agricultural machinery
Linear solenoids are used in hydraulic control blocks to actuate switching valves precisely and reliably. In construction and agricultural machinery, they control the flow of hydraulic fluid, allowing functions such as lifting, lowering or swivelling to be performed. Thanks to their fast response time and high accuracy, they enable efficient control of complex movement sequences. Their robust design guarantees reliable operation even under adverse operating conditions such as vibrations, dirt and temperature fluctuations.
Technical requirements
How Magnetbau Schramme solves the technical requirements
Electromagnets in hydraulics must fulfil demanding technical requirements. Linear solenoids require high tensile forces and short response times, often in robust housings for harsh environments. Proportional solenoids require precise actuating forces and linear characteristics for exact valve control.
Hydraulic solenoids must be able to reliably handle high switching cycles and have a compact design. They must be resistant to vibrations, temperature fluctuations and contamination and be designed to be durable and low-maintenance.
- Switching solenoids for actuating valves in construction and agricultural machinery and similar applications
- Proportional solenoids in mobile hydraulic systems for regulating pressure and flow rate
- Linear solenoids in heavy-duty hydraulic systems for lifting and lowering in forklift trucks
- Proportional solenoids in agricultural technology for controlling attachments
- And many more
More information about electromagnets in the hydraulics sector
1. Solenoid types
Solenoids, reversing solenoids, double solenoids, switching solenoids, proportional solenoids, solenoid valves and valve solenoids are mainly used in the field of hydraulics. They control hydraulic valves, regulate the flow of fluids and enable precise movement and pressure control. These components impress with their reliability, high load capacity and adaptability to harsh operating conditions such as vibrations, dirt and temperature fluctuations.
2 Industry-specific technical requirements
Electromagnetic drives in industrial and mobile hydraulics must fulfil high requirements in terms of precision, reliability and robustness. They are often manufactured on the basis of the requirements of ISO 9001 (quality management), which ensures continuous improvement of processes and product quality. Important technical requirements typically include a dynamic pressure tightness of up to 350 bar to prevent hydraulic fluid from escaping. In addition, they must be vibration-resistant and shock-proof in order to withstand the harsh conditions in construction machinery or agricultural vehicles. The size and actuating force of the solenoids must be precisely matched to the respective hydraulic systems.
In addition, temperature resistance and durability with a high number of switching cycles are crucial to ensure high operational reliability and minimise maintenance requirements.
3. special features
The hydraulics industry is characterised by its specialisation in powerful, precise and reliable drive systems that operate under extreme conditions such as high pressures, temperatures and vibrations. The requirements for pressure tightness, durability and robustness set it apart from other industries and make hydraulic systems indispensable for applications in construction, agricultural and mobile machinery.
Electromagnets in hydraulics - Questions & Answers
How does a solenoid work in hydraulic control blocks for the precise actuation of valves?
A solenoid in hydraulic control blocks works by generating a magnetic field that attracts an iron piston (also known as an armature). This movement actuates a valve that controls the hydraulic pressure or volume flow. In construction and agricultural machinery, the lifting magnet is controlled so precisely that it enables fast and exact reactions, such as lifting or lowering loads. High solenoid forces and fast response times are crucial for the efficiency of the machines.
What are the typical operating pressures for electromagnets in hydraulics?
Electromagnets in hydraulics often have to be able to handle dynamic operating pressures of up to 350 bar or more, depending on the application and specific requirements. They are designed to function reliably even at high pressures while providing the required precision and control. Static pressure requirements can often exceed 1000 bar .
Which standards are relevant for electromagnets in hydraulics?
Electromagnets in hydraulics often have to be developed and produced on the basis of ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management) and specific industry standards for hydraulic systems. These standards ensure high quality, precision and environmental compatibility in production and operation, which is particularly important for applications in demanding industrial and mobile environments.
How is the service life of electromagnets in hydraulic systems guaranteed?
The service life of electromagnets is extended by robust designs, regular maintenance and the use of high-quality materials. They are designed to work reliably even under extreme conditions such as high temperatures, vibrations and pressures. Proper installation and regular inspection of components also help to maximise service life.
Which control systems are used for solenoids in hydraulic systems?
Solenoids in hydraulic systems are usually controlled by proportional valves or single/multiple valves. These control systems enable precise adjustment of the magnetic field, which ensures exact control of fluid flow and pressure in hydraulic systems. In modern systems, digital control is also often integrated to optimise efficiency and performance.