Rapid development, validation & industrialisation.
Holding solenoids
Are you looking for a suitable partner for high-quality solenoids? Magnetbau Schramme is the right place for you! As experts in the development and manufacture of customised holding solenoids, we offer innovative and precise solutions that are perfectly tailored to your individual requirements.
You can rely on our many years of experience and expertise to make your project a success.
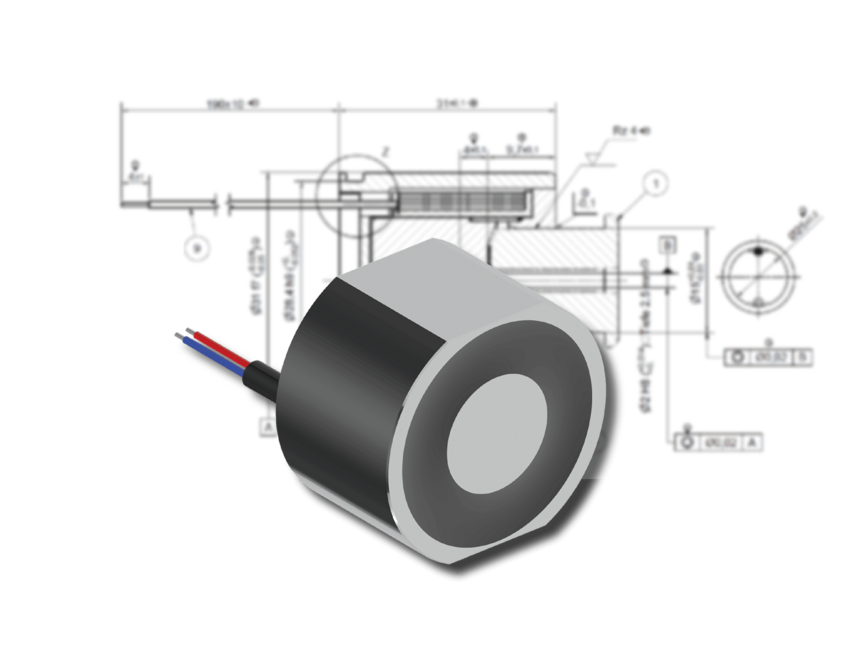
Development and production of holding solenoids
Our performance and expertise. Your success.
Magnetbau Schramme is your competent partner for the development and series production of electromagnets. Thanks to our comprehensive technical expertise and many years of experience, we offer customised solutions that are precisely tailored to your specific requirements. From the concept phase to series production, we accompany you through the entire development process and ensure seamless implementation at every stage of the project.
Contact us today and let our experts advise you individually.
Please note!
Please note that we do not have any standard products. The following holding solenoids are merely examples of customer projects realised in series.
Technical data - Holding solenoids
Experience plenty of different possibilities.
A holding solenoid is an electromagnet that holds metallic objects by magnetic attraction. This holding force depends on the design of the holding solenoid and is generated either when current is applied or when de-energised. Holding solenoid are often used in industrial applications for positioning, holding or fixing.
Do you have any questions about our technical data or other details that you would like to discuss? Please feel free to contact us.
| Sizes / types | No limitation, up to a max. construction weight of 15kg. |
| Nominal voltage range | 6V, 12V, 24V, 36V and others |
| Holding force | up to 5000N |
| Protection class / protection type | IP6K9K |
| Electrical connection | Free stranded wires, surface-mounted connectors, integrated (moulded) connectors, etc. |
| Special features | Seawater-resistant, High energy density, Patented technology |
Development & series production
Magnetbau Schramme is your specialist in the development and production of customised holding solenoids.


Alexander Grischin
Sales Manager
- Requirements analysis
- Feasibility assessment
- Product concept
- Calculation, simulation
- Individual parts, assemblies
- Final assembly
- Functional test
- Proof of technical suitability
- Tools, equipment
- Quality, logistics
- Procurement, production
- Assembly, EOL testing
Electromagnet application example
Safety switch
A bistable reversing solenoid is used in safety switches with guard locking to reliably lock safety doors and only release them after dangerous machine movements have stopped. The bistable function enables the interlock to be held in both positions without a constant supply of energy, which saves energy and increases operational safety. This ensures protection against tampering, as required by EN ISO 14119, and enables safe and efficient machine operation. Ideal for applications with high safety requirements.
More information about holding solenoids
How holding solenoids work
Holding solenoids are electromagnets that are specially developed to hold or release metallic objects. They are used in various areas, from industrial automation systems to safety technology.
- Their mode of operation is based on the principle of magnetic attraction, which is controlled by electric current. At the core of the electromagnet is a coil that generates a magnetic field when current flows. This magnetic field attracts ferromagnetic materials such as iron or steel and holds them in place. When the current is switched off, the magnetic field disappears and the holding solenoid releases the object.
- An important advantage of holding solenoids is their controllable holding force, which can be regulated by the current. They are robust, energy-efficient and versatile, as they are produced in numerous sizes and shapes to meet individual requirements.
Designs and types of holding solenoids
- Square holding solenoids: These electromagnets have a rectangular cross-section. Their compact design makes them ideal for applications where space is limited. They can be easily integrated into various customer applications and offer a reliable holding force that is activated when energised or de-energised, depending on the design and control mechanism.
- Round holding solenoids: With their cylindrical cross-section, these holding solenoids are often more cost-efficient as they are manufactured from housing components that require less material. The round design ensures an even distribution of the magnetic field and thus guarantees a precise and reliable holding force for various industrial applications.
Holding solenoid performance parameters
- Holding force: The holding force of a holding solenoid is typically between 50 and 5000N (Newton), depending on the design and size of the magnet. This force determines how much weight the magnet can hold under ideal conditions, which is crucial for industrial applications.
- Operating voltage: Electric holding solenoid are often operated with operating voltages of 12V, 24V or 48V. The voltage selected influences the strength of the magnetic field generated and therefore the holding force that the magnet can provide.
- Power consumption: The power consumption usually varies between 5W and several hundred W, depending on the holding force and the size of the solenoid. This is an important factor for the energy efficiency and operating costs of the system.
- Duty cycle: Many holding solenoids have a duty cycle of 100 %, which means that they can be operated continuously, while other models are designed for intermittent operation with a lower duty cycle. These values are important to avoid overheating and damage to the holding solenoid.
- Response times: Electromagnetic clamps usually have response times of 50 ms to 200 ms to build up or switch off the magnetic field. This fast response time enables flexible use in applications that require frequent switching on and off.
- Protection class (IP class): Holding solenoids often have a protection class of IP54 (dustproof and splashproof) or IP65 (dustproof and protected against water jets). This classification is important for use in harsh or damp environments.
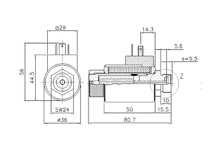
Structure of the holding solenoid
- Housing: The housing is usually made of robust plastic or metal. It protects the internal components and ensures the stability and durability of the holding solenoid. The housing can also ensure that the solenoid can be mounted in different positions.
- Coil: The coil consists of copper wire, which is usually wound on a bobbin. When an electric current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that generates the holding force.
- Electrical connection: The power supply can be a direct current source or a power supply unit, depending on the operating voltage of the electromagnet. It supplies the electrical current required to activate the coil and generate the magnetic field.
- Control elements: These include switches, relays or electronic controls. They control the current flow to the coil and thus the switching on and off of the holding solenoid.
Holding solenoid applications
- Industry and manufacturing: In industry and manufacturing, they are often used to hold workpieces in place during machining or assembly, ensuring precise positioning that increases efficiency in production. They are also used in automation technology as holding devices for robots and machines to transport, hold or store parts securely.
- Transport and logistics: In the transport and logistics sector, holding solenoids are used to hold loads on transport trolleys or in storage facilities to ensure safety during transport. They are also used in conveyor systems, where they hold goods in position during transport.
- Security technology: In security technology, electromagnets are used in anti-theft systems to secure goods in shops and in locking systems where they lock doors or windows. In the household, they are used in appliances such as washing machines and dishwashers to secure door mechanisms.
- Medical technology: In medical technology, holding solenoids support diagnostic devices, particularly in imaging procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They are also important in power generation, for example in wind turbines, where they contribute to the efficient operation of generators.
Control and regulation of holding solenoids
- Electronic control: The electronic control of a solenoid regulates the current supply to the solenoid coil to activate or deactivate the holding force. Simple systems use switches or relays, while more complex systems integrate microcontrollers or programmable logic controllers (PLCs). These systems can manage different operating modes, such as switching the solenoid on and off and time-controlled sequences.
- Pulse width modulation (PWM): With PWM control, the power of the holding solenoid is regulated by rapidly switching the current on and off with a variable pulse length. This technology makes it possible to control the average voltage, which enables precise adjustment of the holding force. PWM saves energy and can prevent overheating, as the solenoid does not have to be operated continuously under full load, which is advantageous in precise applications.
- Sensor integration: Sensors are often integrated into the control of holding solenoid in order to monitor the holding force or position. Position sensors such as Hall sensors provide feedback on the position of the armature plate, while force sensors measure the holding force exerted.
Environmental requirements for holding solenoids
- Temperature range: Holding solenoids must work reliably in a wide temperature range from -40 °C to +150 °C without compromising their performance. High temperatures can lead to overheating and loss of magnetic properties, while very low temperatures can make the material structure brittle. It is therefore crucial that the materials used and the design of the holding magnet are suitable for the specified temperature range.
- Types of protection: Depending on the application environment, electromagnets are equipped with different types of protection (e.g. IP protection classes) to protect them from dust, moisture and other environmental influences. These protective measures are crucial to ensure the long-term functionality and reliability of the solenoid under demanding operating conditions.
Holding solenoids - Questions & Answers
What is the difference between a holding solenoid and a linear solenoid?
Holding solenoids generate a magnetic field that usually makes them adhere to metallic surfaces, which makes them ideal for applications for fastening or securing objects. In contrast, linear solenoids generate a linear movement by applying an electric current, which is used to raise or lower objects. While holding solenoids have simple designs, linear solenoids are more complex as they contain moving components.
In which areas is the holding solenoid most frequently used?
Holding solenoids are often used in automation technology, where they are used to securely fasten and position workpieces in manufacturing processes. They are also used in household applications, such as holding tools or as fastening elements for decorations.
What components are holding solenoids usually made up of?
Electromagnets mainly consist of an electromagnet, which consists of a copper coil wound on a bobbin. The core, often made of iron or a similar material, strengthens the magnetic field when an electric current flows through the coil. In addition to the coil and core, solenoids are sometimes equipped with a control unit that regulates the current flow and controls the activation or deactivation of the solenoid. Many models also have housings made of non-magnetic materials that protect the solenoid and increase safety. Finally, electromagnets can be provided with a special coating to prevent corrosion and extend the service life of the device.
How long is the service life of a holding solenoid and what factors influence it?
The service life of a holding solenoid can range from several years to decades, depending on the quality of the material used and the operating conditions. Factors that influence the service life include temperature, humidity, mechanical loads and the type of use, such as frequent demagnetisation or aggressive chemical environments. Suitable storage and handling can also contribute to extending the service life of holding solenoids.
How does the connection of the holding solenoid to the customer interface work?
A holding solenoid is typically connected to the customer interface via mechanical fastenings or by using adhesive surfaces that enable a stable connection to other components. In many applications, the solenoid is activated or deactivated via electrical or electronic control systems to ensure targeted utilisation. In addition, sensors can be integrated to monitor the status of the magnet and enable seamless communication with the overall system.
What is the difference between a holding solenoid and a permanent magnet?
The main difference between electromagnets and permanent magnets is that electromagnets require an electric current to generate a magnetic field, while permanent magnets generate their magnetic field permanently without an external energy source. Electromagnetic holding solenoids can be activated or deactivated by controlling the current flow, which enables flexible use, while permanent magnets are always magnetic. In addition, electromagnets can often generate stronger magnetic forces, while permanent magnets are generally more compact and easier to handle.