ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certified as developer & producer of electromagnets.
Security technology
Discover how our innovative electromagnet solutions and pioneering technologies are shaping the future of safety technology.

Use of electromagnets
Precision and strength: electromagnets optimise safety technology
Electromagnets, holding magnets and various linear solenoids are central components in safety technology and offer reliable, flexible solutions for the protection of buildings and systems.
Application examples for electromagnets in safety technology
- Holding solenoid in safety doors
- Bistable reversible solenoid in safety switches & locking systems
- Linear solenoids in building doors and machine doors
- And many more
Precision and reliability in demanding applications
Electromagnetic door locks and holding solenoids secure escape and access doors, but can be automatically unlocked in an emergency. In access control systems, they enable precise control of turnstiles and swing doors. In addition, linear solenoids are used in locking mechanisms of safes and security containers to prevent tampering and enable authorized access.
Electromagnets also play an important role in fire protection systems by keeping fire doors open and closing them automatically in the event of an alarm. These versatile magnetic solutions increase security and enable robust control in sensitive areas.
Your advantages with Schramme
Development and production of electromagnets in safety technology
Magnetbau Schramme is your reliable partner for the development and series production of high-quality electromagnets in safety technology. With decades of experience, we offer customised solutions that meet the highest precision, reliability and safety standards.
Our expertise ranges from the initial idea to series production, and thanks to our flexible production processes, we can implement individual requirements quickly and efficiently. You can rely on quality "Made in Germany" for your innovative safety technology applications.
More than 50 years of experience in the development & series production of electromagnets.
CNC, welding, soldering, injection moulding assembly (ESD / clean room) and much more.


Alexander Grischin
Sales Manager
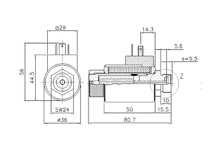
Electromagnet application example
Safety switch
A bistable reversing solenoid is used in safety switches with guard locking to reliably lock safety doors and only release them after dangerous machine movements have stopped. The bistable function enables the interlock to be held in both positions without a constant supply of energy, which saves energy and increases operational safety. This ensures protection against tampering, as required by EN ISO 14119, and enables safe and efficient machine operation. Ideal for applications with high safety requirements.
Technical requirements
How Magnetbau Schramme solves the technical requirements
In safety technology, electromagnets, holding solenoids and linear solenoids must fulfil particularly high requirements in terms of reliability, load capacity and precision. They must be robust against temperature fluctuations, moisture and mechanical stress in order to function perfectly in critical situations such as access control, emergency systems and fire protection applications.
Safety-relevant applications require high holding force, reliable unlocking mechanisms and compliance with safety-critical standards such as SIL (Safety Integrity Level), PL (Performance Level) and IECEx to prevent tampering and ensure long-term operational safety in sensitive environments.
- Holding solenoid in safety doors
- Bistable reversible solenoid in safety switches & locking systems
- Linear solenoids in building doors and machine doors
- And many more
Further information about electromagnets in safety technology
1. Electromagnet types
Electromagnets, holding solenoids, linear solenoids, switching solenoids and proportional solenoids are mainly used in safety technology. They are used in access control systems, interlocks and fire protection applications. Solenoid valves, valve solenoids and electromagnetic brakes are also used, for example, to control safety mechanisms and emergency systems in order to ensure reliable operational and tamper protection.
2. Industry-specific technical requirements
In safety technology, electromagnets and linear solenoids must fulfil particularly strict requirements in order to ensure operational safety in safety-critical applications. They require high holding and pulling forces for reliable locking and precise control in access control and emergency systems. The solenoids must also be resistant to temperature fluctuations, moisture and vibrations in order to work reliably in demanding environments. Industry-specific standards such as SIL (Safety Integrity Level), PL (Performance Level) and IECEx are essential here in order to guarantee tamper resistance and long-term functionality.
Flexibility in control and a fast response time are also important to enable immediate release or locking in an emergency.
3. Special features
In safety technology, electromagnets must be particularly tamper-proof and fulfil the strictest certifications for personal protection. They also require a fail-safe function for automatic unlocking in the event of a power failure, which is often less central in other industries. High reliability for emergency releases is also crucial.
Electromagnets in the field of medical technology - Questions & Answers
What does functional safety according to IEC 62061 - Safety Integrity Level (SIL) describe?
Functional safety in accordance with IEC 62061 assesses the reliability of safety-critical control systems in machines by means of the Safety Integrity Level (SIL). SIL defines the risk reduction requirements for systems and their probability of safety-critical failures. The higher the SIL value (from SIL 1 to SIL 3 for machines), the stricter the requirements for fault detection and failure safety in order to ensure personal and operational safety in automated processes.
For which specific function is the bistable reversible solenoid relevant in safety-related applications?
The bistable reversible solenoid is particularly relevant in safety-related applications for reliable locking and emergency release. As it can hold two stable positions without a permanent power supply, it is ideal for escape doors and access control systems. In the event of a power failure, the last position is retained, which saves energy in critical security applications and ensures tamper-proof locking.
What are the legal requirements and standards for electromagnetic drives in safety technology?
Strict standards apply to electromagnetic drives in safety technology: SIL (IEC 61508) and PL (EN ISO 13849-1) define safety integrity and performance levels, while IECEx ensures safe operation in potentially explosive atmospheres. The EMC Directive (2014/30/EU) and the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) regulate electromagnetic compatibility and machine safety. VDE 0580 sets requirements for general safety and functionality. These standards guarantee reliable, tamper-proof use.
What advantages do electromagnets offer in safety technology?
In safety technology, electromagnets offer high reliability, fast response times and flexible control options. They enable precise locking and controlled unlocking, for example in access control or emergency systems. Thanks to their high holding force and low maintenance requirements, they ensure long-term security. They are also tamper-proof and energy-saving thanks to functions such as fail-safe, which is particularly important in safety-critical applications.
How do linear solenoids differ from holding solenoids in safety applications?
Linear solenoids are mostly used for locking and unlocking applications that require high precision and a quick response. Holding solenoids, on the other hand, offer permanent holding force for safety locks that are only released in an emergency. Both types of electromagnets are indispensable in access control, escape doors and fire protection systems, but have different strengths.